TREATMENTS
Gum Depigmentation Treatment in Lahore
Gum Depigmentation
Gum depigmentation, also known as gum bleaching or gingival depigmentation, is a cosmetic dental procedure designed to reduce or eliminate the appearance of dark or pigmented gums. The dark coloration of the gums is often caused by an excess of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin and hair color.
- Functional Impairment
- Aesthetic Concerns
- Speech Difficulties
- Preventing Tooth Migration
- Preserving Bone Health
- Improving Oral Health
- List Item #1
- List Item #2
- List Item #3
Types Of Gum Depigmentation

Topical Anesthesia
To ensure patient comfort, a topical anesthetic is applied to the gums to numb the treatment area.
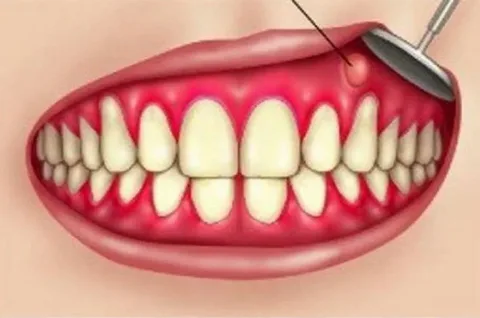
Laser Gum Depigmentation
A dental laser is used to remove the pigmented layer of the gums. This is a precise and effective method that also helps in sealing blood vessels, reducing bleeding, and promoting faster healing.
Surgical Depigmentation
In this method, the dentist uses a scalpel or laser to remove the pigmented layer from the gums. This technique may be preferred in cases where there is a significant amount of pigmentation to be removed.
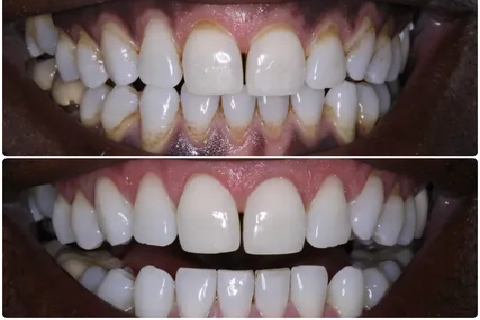
Chemical Depigmentation
Certain chemical agents, such as a concentrated acid solution, may be applied to the gum tissue to peel away the pigmented layer. This method requires careful application to avoid damage to surrounding tissues.
CAUSES OF GUMS DEPIGMENTATION
Dentistry focused on providing oral health care to children. Pediatric dentistry is driven by the recognition of the unique needs and considerations associated with the dental care of infants, children, and adolescents.if you meant to inquire about the factors that lead to the need for pediatric dentistry or the common issues addressed in this field,
Ethnicity
Gum pigmentation can vary among individuals of different ethnic backgrounds.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, pigmentation.
Smoking
Smoking or tobacco use is associated with changes in oral pigmentation.
Medications
Some medications may cause changes in pigmentation as a side effect.
Gums Depigmentation
Symptoms of Gums Depigmentation
- Discomfort or Sensitivity
- Swelling
- Gum Disease
- Healing Time
- Dental Injuries and Trauma
- Changes in Gum Color
How To Take Care Missing Teeth
Taking care of your oral health, especially when you have missing teeth, is important to prevent complications and maintain overall well-being. Here are some tips on how to care for missing teeth:
Floss Regularly: Floss between your remaining natural teeth and around dental appliances to remove plaque and prevent gum disease. If you have dental bridges or implants, use floss threaders or interdental brushes for effective cleaning.
Use an Antiseptic Mouthwash: Rinse your mouth with an antiseptic or fluoride mouthwash to help control bacteria and maintain oral hygiene. Consult your dentist for recommendations based on your specific needs.
Visit Your Dentist Regularly: Schedule regular dental check-ups, even if you have missing teeth. Your dentist can monitor the health of your remaining teeth, assess your gum health, and address any concerns promptly.
Consider Dental Appliances If you have missing teeth, your dentist may recommend dental appliances such as bridges, dentures, or implants to restore function and aesthetics. Follow your dentist’s instructions for care and maintenance of these appliances.
FAQs
Gum depigmentation is a cosmetic dental procedure designed to reduce or eliminate the dark pigmentation of the gums, often caused by an excess of melanin.
Some individuals seek gum depigmentation for aesthetic reasons, as they may be dissatisfied with the appearance of dark or pigmented gums and desire a more uniform and aesthetically pleasing smile.
Pigmented gums are generally healthy and not a sign of poor oral health. Gum depigmentation is a cosmetic procedure and is not performed for medical reasons.
The primary cause of pigmented gums is an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin and hair color. Factors such as genetics, ethnicity, hormonal changes, smoking, medications, and inflammation can contribute to gum pigmentation.
Gum depigmentation is usually well-tolerated, and discomfort is typically minimal. Topical anesthesia is often applied to numb the treatment area and ensure patient comfort.
The duration of the procedure varies depending on the chosen method and the extent of pigmentation. Generally, it can be completed within a relatively short time, often in a single appointment.

